Our Mission Repurposing Medicines in Africa
Finding new therapeutic uses for existing drugs—is a cost-effective strategy to address health challenges in Africa. This approach can help tackle neglected diseases, improve access to affordable treatments, and strengthen healthcare systems. Here’s how it applies to global health in Africa:
WHAT WE DO
Sifa Biosciences was founded in 2020 to harness science, technology, and innovation to discover and develop medicines for global health. The WHO constitution states, “Health is a complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity”.
In line with the WHO definition of health, Sifa Biosciences aims to take action in support of mission-relevant sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Read More
Our Approch
Repurposing medicines offers a promising approach to tackling diseases disproportionately affecting Africa, particularly in the context of limited resources and the high burden of infectious and neglected diseases. It holds significant potential to expand treatment options and improve health outcomes, especially when new drugs and treatments are slow to develop.
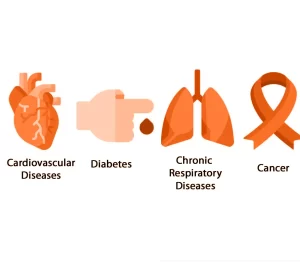
- For chronic diseases: With the growing prevalence of non-communicable diseases like cancer and cardiovascular conditions, repurposing existing treatments could offer a faster route to addressing these health concerns in the region.
- Cost-effectiveness: In low-resource settings, where funding for new drug development is scarce, repurposing can provide access to life-saving treatments without the high costs of traditional drug discovery
![]()
Challenges in Drug Repurposing
Foucus on Africa
Drug repurposing, the strategy of identifying new therapeutic uses for existing medications, has gained significant traction globally and holds particular promise for addressing health challenges in Africa. This approach offers a cost-effective and time-efficient alternative to traditional drug development, which is especially beneficial in resource-limited settings.
1
Navigating the regulatory landscape for new indications of existing drugs can be complex, often requiring substantial evidence to gain approval.
2
Determining patent rights and market exclusivity for repurposed drugs can be legally intricate, potentially deterring investment.
3
Securing financial support for repurposing studies can be challenging, particularly when the potential for high financial returns is uncertain.
Future Prospects and Collaborative Efforts
Collaborative initiatives are essential to overcome these challenges. Organizations like the Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative (DNDi) have been instrumental in developing treatments for diseases prevalent in Africa by repurposing existing drugs. For instance, DNDi’s fixed-dose combination therapy for malaria has been widely adopted across the continent.
Furthermore, the establishment of drug repurposing hubs and databases facilitates the identification of candidate drugs for new therapeutic uses. These platforms provide researchers with access to comprehensive information on existing medications, streamlining the repurposing process.
Conclusion
Drug repurposing presents a viable and efficient strategy to address the healthcare challenges in Africa. By leveraging existing medications, this approach can expedite the delivery of effective treatments to populations in need. Continued investment in research, coupled with supportive regulatory frameworks and collaborative efforts, will be crucial in realizing the full potential of drug repurposing on the continent.
Disease Areas
Want to Explore Click here